Newly released Federal Trade Commission data show that consumers reported losing more than $10 billion to fraud in 2023, marking the first time that fraud losses have reached that benchmark. This marks a 14% increase over reported losses in 2022.
Consumers reported losing more money to investment scams—more than $4.6 billion—than any other category in 2023. That amount represents a 21% increase over 2022. The second highest reported loss amount came from imposter scams, with losses of nearly $2.7 billion reported. In 2023, consumers reported losing more money to bank transfers and cryptocurrency than all other methods combined.
"Digital tools are making it easier than ever to target hard-working Americans, and we see the effects of that in the data we're releasing today,” said Samuel Levine, Director of the FTC’s Bureau of Consumer Protection. “The FTC is working hard to take action against those scams."
The FTC received fraud reports from 2.6 million consumers last year, nearly the same amount as 2022. The most commonly reported scam category was imposter scams, which saw significant increases in reports of both business and government impersonators. 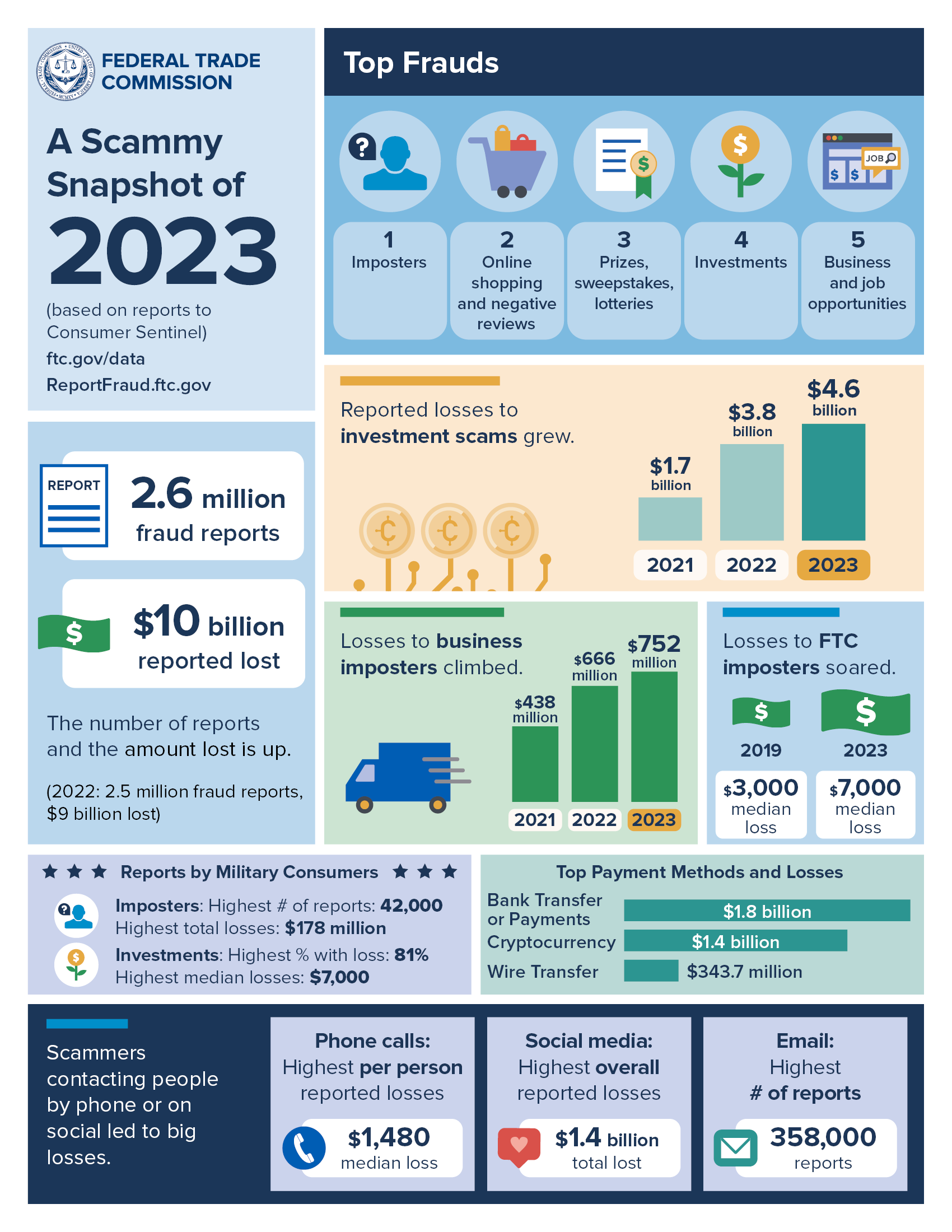
Online shopping issues were the second most commonly reported in the fraud category, followed by prizes, sweepstakes, and lotteries; investment-related reports; and business and job opportunity scams.
Another first is the method scammers reportedly used to reach consumers most commonly in 2023: email. Email displaced text messages, which held the top spot in 2022 after decades of phone calls being the most common. Phone calls are the second most commonly reported contact method for fraud in 2023, followed by text messages.
The Commission monitors these trends carefully, and is taking a comprehensive approach to detect, halt, and deter consumer fraud, including in 2023 alone:
- Leading the largest-ever crackdown on illegal telemarketing: The FTC joined more than 100 federal and state law enforcement partners nationwide, including the attorneys general from all 50 states and the District of Columbia in Operation Stop Scam Calls, a crackdown on illegal telemarketing calls involving more than 180 actions targeting operations responsible for billions of calls to U.S. consumers.
- Proposing a ban on impersonator fraud: The FTC is in the final stages of a rulemaking process targeting business and government impersonation scams.
- Cracking Down on Investment Schemes: The FTC has brought multiple cases against investment and business opportunity schemes, including Wealthpress, Blueprint to Wealth, Traffic and Funnels, Automators and Ganadores.
- Confronting Emerging Forms of Fraud: The FTC has taken steps to listen to consumers and build knowledge and tools to fight emerging frauds. For example, the FTC announced a challenge in 2023 to help promote the development of ideas to protect consumers from the misuse of artificial intelligence-enabled voice cloning for fraud and other harms.
- Stepping up CAN-SPAM Enforcement: The FTC is using its authority under the CAN-SPAM Act to rein in unlawful actions, including in cases against Publishers Clearing House and Experian.
- Reaching Every Community: The FTC has expanded its ability to hear directly from consumers in multiple languages through the Consumer Sentinel Network.
The FTC’s Consumer Sentinel Network is a database that receives reports directly from consumers, as well as from federal, state, and local law enforcement agencies, the Better Business Bureau, industry members, and non-profit organizations. More than 20 states contribute data to Sentinel.
Sentinel received 5.4 million reports in 2023; these include the fraud reports detailed above, as well as identity theft reports and complaints related to other consumer issues, such as problems with credit bureaus and banks and lenders. In 2023, there were more than 1 million reports of identity theft received through the FTC’s IdentityTheft.gov website.
The FTC uses the reports it receives through the Sentinel network as the starting point for many of its law enforcement investigations, and the agency also shares these reports with approximately 2,800 federal, state, local, and international law enforcement professionals. While the FTC does not intervene in individual complaints, Sentinel reports are a vital part of the agency’s law enforcement mission and also help the FTC to warn consumers and identify fraud trends it is seeing in the data.
A full breakdown of reports received in 2023 is now available on the FTC’s data analysis site at ftc.gov/exploredata. The data dashboards there break down the reports across a number of categories, including by state and metropolitan area, and also provide data from a number of subcategories of fraud reports.
The Federal Trade Commission works to promote competition and protect and educate consumers. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Learn more about consumer topics at consumer.ftc.gov, or report fraud, scams, and bad business practices at ReportFraud.ftc.gov. Follow the FTC on social media, read consumer alerts and the business blog, and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts.
